Nylon fabric socks have surged in popularity due to their durability and moisture-wicking properties, making them ideal for athletic activities. However, the hidden truth behind their production raises environmental concerns. The global Nylon Socks market size was valued at USD Million in 2022 and is projected to reach USD Million by 2028, with a CAGR of XX% during 2022-2028. This growth has significant implications for the environment, prompting a closer look at the sustainability of nylon sock production.
The Production Process of Nylon Fabric Socks
Nylon fabric socks have become a staple in the world of fashion and sports due to their remarkable properties, but the process of creating these socks has significant implications for the environment. Understanding the production process is crucial in evaluating its environmental impact.
From Synthetic Fibers to Socks
The creation of nylon fibers involves an intricate and energy-intensive process. Synthetic fibers, including nylon, are derived from petrochemicals through a series of complex chemical reactions and high-temperature treatments. These procedures highlight the importance of taking a responsible approach to lowering the carbon footprint associated with the manufacture of nylon. The transformation from raw materials to nylon fibers requires substantial energy consumption and emits greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental degradation.
Weaving these nylon fibers into socks involves various manufacturing stages, including spinning, knitting, and finishing processes. The weaving process consumes additional energy and resources, further amplifying the environmental impact. It’s essential to recognize that each step in this journey significantly contributes to the overall ecological footprint of nylon fabric socks.
The creation of nylon fibers
- The extraction and refinement of petrochemicals into polymer chips.
- Polymer chips are melted at high temperatures and extruded into fine filaments.
- These filaments are then spun into yarns using specialized machinery.
Weaving into socks
- Spinning: Converting yarns into threads suitable for knitting.
- Knitting: Utilizing advanced knitting machines to create seamless sock designs.
- Finishing: Applying treatments for moisture-wicking properties and durability enhancement.
Energy and Chemical Use
The production of nylon fabric socks heavily relies on energy-intensive manufacturing processes that contribute to environmental degradation. Various studies have highlighted the negative impacts associated with this production method:
Scientific Research Findings:
- Environmental Impact of Nylon Production: The energy-intensive production procedures, which include complex chemical reactions and high-temperature treatments, highlight the importance of taking a responsible approach to lowering the carbon footprint connected to the manufacture of nylon.
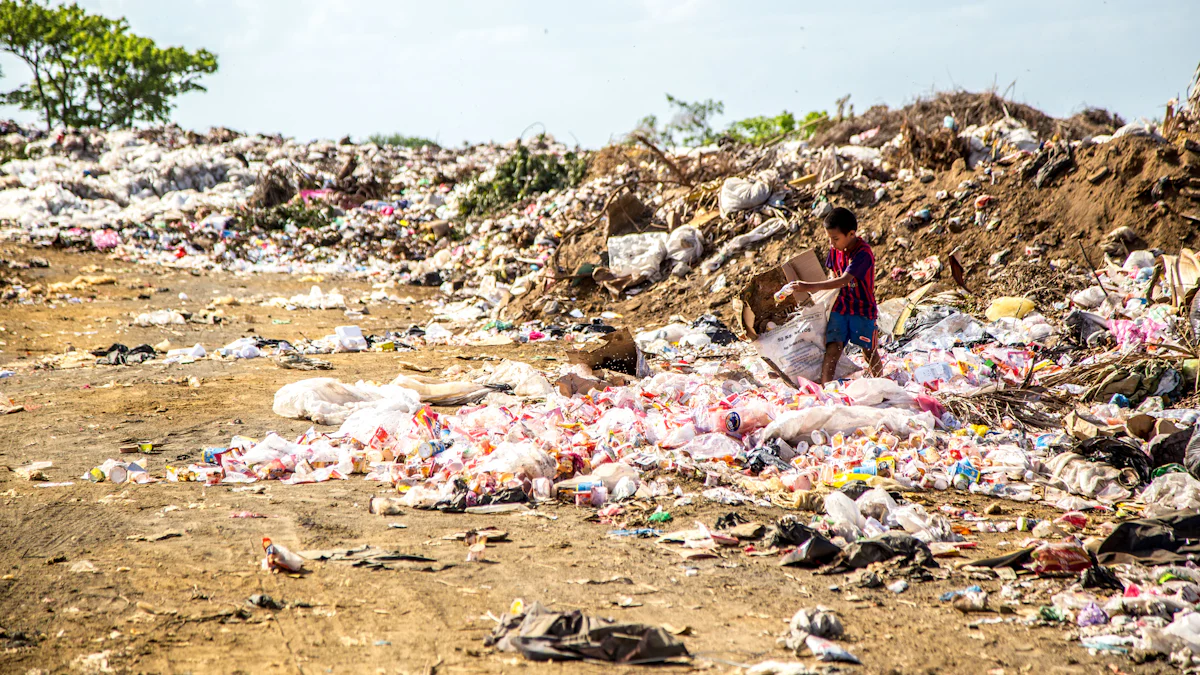
- Negative Impacts of Nylon Fabric on the Environment: Nylon has many major negative impacts on the environment, including non-biodegradability, release of toxic fumes when burned, and water pollution from dyes used in its production.
- Environmental Consequences of Nylon Production: Producing nylon creates nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas that is 300 times more potent than carbon dioxide. Manufacturing nylon also requires large amounts of water and energy, further contributing to environmental degradation and global warming.
Energy consumption in manufacturing
The production process demands substantial amounts of electricity for operating machinery, heating elements during extrusion processes, as well as powering other equipment involved in spinning and weaving activities. This results in increased greenhouse gas emissions due to reliance on non-renewable energy sources such as fossil fuels.
Chemicals in nylon production
Nylon production involves utilizing various chemicals throughout different stages such as polymerization, spinning, dyeing processes which can lead to potential pollution risks if not managed properly. Additionally, it sheds microplastic fibers during both its production phase as well as when it is washed or used by consumers.
The comprehensive understanding provided here emphasizes how vital it is for manufacturers and consumers alike to consider sustainable alternatives that minimize these detrimental effects on our environment while still meeting consumer needs for durable yet eco-friendly products.
In light of the growing demand for nylon fabric socks, a critical examination of their environmental impact is imperative. The extraction of raw materials from petrochemical sources for nylon production necessitates a thorough analysis of its carbon emissions and ecological stress. Additionally, post-consumer disposal poses significant challenges as nylon fabric is non-biodegradable and releases toxic fumes when burned. It’s essential to consider sustainable alternatives to minimize the detrimental effects on our environment while still meeting consumer needs for durable yet eco-friendly products.